ENSO Calculations using Globus Flows
Overview
In this workflow, we combine topics covered in previous Pythia Foundations and CMIP6 Cookbook content to compute the Niño 3.4 Index to multiple datasets, with the primary computations occuring on a remote machine. As a refresher of what the ENSO 3.4 index is, please see the following text, which is also included in the ENSO Xarray content in the Pythia Foundations content.
Niño 3.4 (5N-5S, 170W-120W): The Niño 3.4 anomalies may be thought of as representing the average equatorial SSTs across the Pacific from about the dateline to the South American coast. The Niño 3.4 index typically uses a 5-month running mean, and El Niño or La Niña events are defined when the Niño 3.4 SSTs exceed +/- 0.4C for a period of six months or more.
Niño X Index computation: a) Compute area averaged total SST from Niño X region; b) Compute monthly climatology (e.g., 1950-1979) for area averaged total SST from Niño X region, and subtract climatology from area averaged total SST time series to obtain anomalies; c) Smooth the anomalies with a 5-month running mean; d) Normalize the smoothed values by its standard deviation over the climatological period.
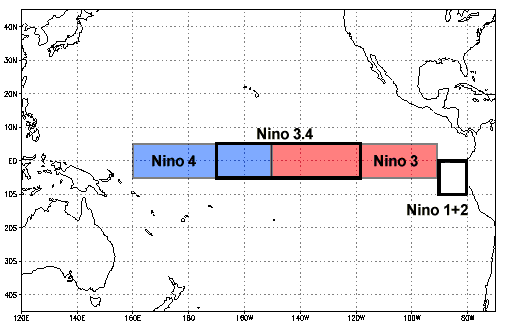
The previous cookbook, we ran this in a single notebook locally. In this example, we aim to execute the workflow on a remote machine, with only the visualizion of the dataset occuring locally.
The overall goal of this tutorial is to introduce the idea of functions as a service with Globus, and how this can be used to calculate ENSO indices.
Prerequisites
Concepts |
Importance |
Notes |
|---|---|---|
Necessary |
||
Necessary |
Interactive Visualization with hvPlot |
|
Helpful |
Familiarity with metadata structure |
|
Neccessary |
Understanding of Masking and Xarray Functions |
|
Dask |
Helpful |
Time to learn: 30 minutes
Imports
import hvplot.xarray
import holoviews as hv
import numpy as np
import hvplot.xarray
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
from intake_esgf import ESGFCatalog
import xarray as xr
import cf_xarray
import warnings
import json
import os
import time
import globus_sdk
from globus_compute_sdk import Client, Executor
from globus_automate_client import FlowsClient
# Import Globus scopes
from globus_sdk.scopes import SearchScopes
from globus_sdk.scopes import TransferScopes
from globus_sdk.scopes import FlowsScopes
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
hv.extension("bokeh")
Accessing our Data and Computing the ENSO 3.4 Index
As mentioned in the introduction, we are utilizing functions from the previous ENSO notebooks. In order to run these with Globus Compute, we need to comply with the following requirements
All libraries/packages used in the function need to be installed on the globus compute endpoint
All functions/libraries/packages need to be imported and defined within the function to execute
The output from the function needs to serializable (ex. xarray.Dataset, numpy.array)
Using these constraints, we setup the following function, with the key parameter being which model (source_id) to compare. Two examples here include The National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) Model CESM2 and the Model for Interdisciplinary Research on Climate (MIROC) Model MIROC6. Valid responses for this exercise include:
ACCESS-ESM1-5EC-Earth3-CCMPI-ESM1-2-LRCanESM5MIROC6EC-Earth3CESM2EC-Earth3-VegNorCPM1
def run_plot_enso(source_id, return_path=False):
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from intake_esgf import ESGFCatalog
import xarray as xr
import cf_xarray
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
def search_esgf(source_id):
# Search and load the ocean surface temperature (tos)
cat = ESGFCatalog(esgf1_indices="anl-dev")
cat.search(
activity_id="CMIP",
experiment_id="historical",
variable_id=["tos"],
source_id=source_id,
member_id='r1i1p1f1',
grid_label="gn",
table_id="Omon",
)
try:
tos_ds = cat.to_dataset_dict()["tos"]
except ValueError:
print(f"Issue with {institution_id} dataset")
return tos_ds
def calculate_enso(ds):
# Subset the El Nino 3.4 index region
dso = ds.where(
(ds.cf["latitude"] < 5) & (ds.cf["latitude"] > -5) & (ds.cf["longitude"] > 190) & (ds.cf["longitude"] < 240), drop=True
)
# Calculate the monthly means
gb = dso.tos.groupby('time.month')
# Subtract the monthly averages, returning the anomalies
tos_nino34_anom = gb - gb.mean(dim='time')
# Determine the non-time dimensions and average using these
non_time_dims = set(tos_nino34_anom.dims)
non_time_dims.remove(ds.tos.cf["T"].name)
weighted_average = tos_nino34_anom.weighted(ds["areacello"].fillna(0)).mean(dim=list(non_time_dims))
# Calculate the rolling average
rolling_average = weighted_average.rolling(time=5, center=True).mean()
std_dev = weighted_average.std()
return rolling_average / std_dev
def add_enso_thresholds(da, threshold=0.4):
# Conver the xr.DataArray into an xr.Dataset
ds = da.to_dataset()
# Cleanup the time and use the thresholds
try:
ds["time"]= ds.indexes["time"].to_datetimeindex()
except:
pass
ds["tos_gt_04"] = ("time", ds.tos.where(ds.tos >= threshold, threshold).data)
ds["tos_lt_04"] = ("time", ds.tos.where(ds.tos <= -threshold, -threshold).data)
# Add fields for the thresholds
ds["el_nino_threshold"] = ("time", np.zeros_like(ds.tos) + threshold)
ds["la_nina_threshold"] = ("time", np.zeros_like(ds.tos) - threshold)
return ds
ds = search_esgf(source_id)
enso_index = add_enso_thresholds(calculate_enso(ds).compute())
enso_index.attrs = ds.attrs
enso_index.attrs["model"] = source_id
return enso_index
Configure Globus Compute
Now that we have our functions, we can move toward using Globus Flows and Globus Compute.
Globus Flows is a reliable and secure platform for orchestrating and performing research data management and analysis tasks. A flow is often needed to manage data coming from instruments, e.g., image files can be moved from local storage attached to a microscope to a high-performance storage system where they may be accessed by all members of the research project.
More examples of creating and running flows can be found on our demo instance.
Setup a Globus Compute Endpoint
Globus Compute (GC) is a service that allows python functions to be sent to remote points, executed, with the output from that function returned to the user. While there are a collection of endpoints already installed, we highlight in this section the steps required to configure for yourself. This idea is also known as “serverless” computing, where users do not need to think about the underlying infrastructure executing the code, but rather submit functions to be run and returned.
To start a GC endpoint at your system you need to login, configure a conda environment, and pip install globus-compute-endpoint.
You can then run:
globus-compute-endpoint configure esgf-test
globus-compute-endpoint start esgf-test
Note that by default your endpoint will execute tasks on the login node (if you are using a High Performance Compute System). Additional configuration is needed for the endpoint to provision compute nodes. For example, here is the documentation on configuring globus compute endpoints on the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility’s Polaris system
https://globus-compute.readthedocs.io/en/latest/endpoints.html#polaris-alcf
endpoint_id = "6836803d-9831-4dc5-b159-eb658250e4bc"
personal_endpoint_id = "92bb829c-9d88-11ed-b579-33287ee02ec7"
Setup an Executor to Run our Functions
Once we have our compute endpoint ID, we need to pass this to our executor, which will be used to pass our functions from our local machine to the machine we would like to compute on.
gce = Executor(endpoint_id=endpoint_id)
gce.amqp_port = 443
gce
Executor<ep_id:6836803d-9831-4dc5-b159-eb658250e4bc; tg_id:None; bs:128>
Test our Functions
Now that we have our functions prepared, and an executor to run on, we can test them out using our endpoint!
We pass in our function name, and the additional arguments for our functions. For example, let’s look at comparing at the NCAR and MIROC modeling center’s CMIP6 simulations.
ncar_task = gce.submit(run_plot_enso, source_id='CESM2')
miroc_task = gce.submit(run_plot_enso, source_id='MIROC6')
The results are started as python objects, with the resultant datasets available using .result()
ncar_ds = ncar_task.result()
miroc_ds = miroc_task.result()
ncar_ds
<xarray.Dataset> Size: 111kB
Dimensions: (time: 1980)
Coordinates:
* time (time) datetime64[ns] 16kB 1850-01-15T13:00:00.000008 ...
month (time) int64 16kB 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ... 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Data variables:
tos (time) float64 16kB nan nan 0.9395 ... -0.5907 nan nan
tos_gt_04 (time) float64 16kB 0.4 0.4 0.9395 1.01 ... 0.4 0.4 0.4
tos_lt_04 (time) float64 16kB -0.4 -0.4 -0.4 ... -0.5907 -0.4 -0.4
el_nino_threshold (time) float64 16kB 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4 ... 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.4
la_nina_threshold (time) float64 16kB -0.4 -0.4 -0.4 ... -0.4 -0.4 -0.4
Attributes: (12/46)
Conventions: CF-1.7 CMIP-6.2
activity_id: CMIP
case_id: 15
cesm_casename: b.e21.BHIST.f09_g17.CMIP6-historical.001
contact: cesm_cmip6@ucar.edu
creation_date: 2019-01-16T21:31:39Z
... ...
sub_experiment_id: none
branch_time_in_parent: 219000.0
branch_time_in_child: 674885.0
branch_method: standard
further_info_url: https://furtherinfo.es-doc.org/CMIP6.NCAR.CESM2.h...
model: CESM2ncar_ds = ncar_task.result()
Plot our Data
Now that we have pre-computed datasets, the last step is to visualize the output. In the other example, we stepped through how to utilize the .hvplot tool to create interactive displays of ENSO values. We will utilize that functionality here, wrapping into a function.
def plot_enso(ds):
el_nino = ds.hvplot.area(x="time", y2='tos_gt_04', y='el_nino_threshold', color='red', hover=False)
el_nino_label = hv.Text(ds.isel(time=40).time.values, 2, 'El Niño').opts(text_color='red',)
# Create the La Niña area graphs
la_nina = ds.hvplot.area(x="time", y2='tos_lt_04', y='la_nina_threshold', color='blue', hover=False)
la_nina_label = hv.Text(ds.isel(time=-40).time.values, -2, 'La Niña').opts(text_color='blue')
# Plot a timeseries of the ENSO 3.4 index
enso = ds.tos.hvplot(x='time', line_width=0.5, color='k', xlabel='Year', ylabel='ENSO 3.4 Index')
# Combine all the plots into a single plot
return (el_nino_label * la_nina_label * el_nino * la_nina * enso).opts(title=f'{ds.attrs["model"]} {ds.attrs["source_id"]} \n Ensemble Member: {ds.attrs["variant_label"]}')
Once we have the function, we apply to our two datasets and combine into a single column.
(plot_enso(ncar_ds) + plot_enso(miroc_ds)).cols(1)
Modify to Run in a Globus Flow
Next, let’s modify our script to:
Search and download ESGF data
Calculate ENSO
Visualize and save the output as an html file
def run_plot_enso(source_id, return_path=False):
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from intake_esgf import ESGFCatalog
import xarray as xr
import cf_xarray
import warnings
import holoviews as hv
import os
import hvplot
import hvplot.xarray
hv.extension('bokeh')
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
def search_esgf(source_id):
# Search and load the ocean surface temperature (tos)
cat = ESGFCatalog(esgf1_indices="anl-dev")
cat.search(
activity_id="CMIP",
experiment_id="historical",
variable_id=["tos"],
source_id=source_id,
member_id='r1i1p1f1',
grid_label="gn",
table_id="Omon",
)
try:
tos_ds = cat.to_dataset_dict()["tos"]
except ValueError:
print(f"Issue with {institution_id} dataset")
return tos_ds
def calculate_enso(ds):
# Subset the El Nino 3.4 index region
dso = ds.where(
(ds.cf["latitude"] < 5) & (ds.cf["latitude"] > -5) & (ds.cf["longitude"] > 190) & (ds.cf["longitude"] < 240), drop=True
)
# Calculate the monthly means
gb = dso.tos.groupby('time.month')
# Subtract the monthly averages, returning the anomalies
tos_nino34_anom = gb - gb.mean(dim='time')
# Determine the non-time dimensions and average using these
non_time_dims = set(tos_nino34_anom.dims)
non_time_dims.remove(ds.tos.cf["T"].name)
weighted_average = tos_nino34_anom.weighted(ds["areacello"].fillna(0)).mean(dim=list(non_time_dims))
# Calculate the rolling average
rolling_average = weighted_average.rolling(time=5, center=True).mean()
std_dev = weighted_average.std()
return rolling_average / std_dev
def add_enso_thresholds(da, threshold=0.4):
# Conver the xr.DataArray into an xr.Dataset
ds = da.to_dataset()
# Cleanup the time and use the thresholds
try:
ds["time"]= ds.indexes["time"].to_datetimeindex()
except:
pass
ds["tos_gt_04"] = ("time", ds.tos.where(ds.tos >= threshold, threshold).data)
ds["tos_lt_04"] = ("time", ds.tos.where(ds.tos <= -threshold, -threshold).data)
# Add fields for the thresholds
ds["el_nino_threshold"] = ("time", np.zeros_like(ds.tos) + threshold)
ds["la_nina_threshold"] = ("time", np.zeros_like(ds.tos) - threshold)
return ds
def plot_enso(ds):
el_nino = ds.hvplot.area(x="time", y2='tos_gt_04', y='el_nino_threshold', color='red', hover=False)
el_nino_label = hv.Text(ds.isel(time=40).time.values, 2, 'El Niño').opts(text_color='red',)
# Create the La Niña area graphs
la_nina = ds.hvplot.area(x="time", y2='tos_lt_04', y='la_nina_threshold', color='blue', hover=False)
la_nina_label = hv.Text(ds.isel(time=-40).time.values, -2, 'La Niña').opts(text_color='blue')
# Plot a timeseries of the ENSO 3.4 index
enso = ds.tos.hvplot(x='time', line_width=0.5, color='k', xlabel='Year', ylabel='ENSO 3.4 Index')
# Combine all the plots into a single plot
return (el_nino_label * la_nina_label * el_nino * la_nina * enso).opts(title=f'{ds.attrs["model"]} {ds.attrs["source_id"]} \n Ensemble Member: {ds.attrs["variant_label"]}')
ds = search_esgf(source_id)
enso_index = add_enso_thresholds(calculate_enso(ds).compute())
enso_index.attrs = ds.attrs
enso_index.attrs["model"] = source_id
plot = plot_enso(enso_index)
if return_path:
path = f"{os.getcwd()}/plot.html"
hvplot.save(plot, path)
else:
path = plot
return path
sample = run_plot_enso(source_id="MPI-ESM1-2-LR", return_path=True)
sample
'/Users/mgrover/git_repos/esgf-cookbook/notebooks/plot.html'
Deploy the Function as a Flow
Now, let’s deploy this function within a Globus-Flow!
Configure Authentication
# Set Native App client
CLIENT_ID = '16659080-53cd-45c7-8737-833d3e719f32' # From
native_auth_client = globus_sdk.NativeAppAuthClient(CLIENT_ID)
# Initialize Globus Auth flow with relevant scopes
auth_kwargs = {"requested_scopes": [FlowsScopes.manage_flows, SearchScopes.all, TransferScopes.all]}
native_auth_client.oauth2_start_flow(**auth_kwargs)
# Explicitly start the flow
print(f"Login Here:\n\n{native_auth_client.oauth2_get_authorize_url()}")
Login Here:
https://auth.globus.org/v2/oauth2/authorize?client_id=16659080-53cd-45c7-8737-833d3e719f32&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fauth.globus.org%2Fv2%2Fweb%2Fauth-code&scope=https%3A%2F%2Fauth.globus.org%2Fscopes%2Feec9b274-0c81-4334-bdc2-54e90e689b9a%2Fmanage_flows+urn%3Aglobus%3Aauth%3Ascope%3Asearch.api.globus.org%3Aall+urn%3Aglobus%3Aauth%3Ascope%3Atransfer.api.globus.org%3Aall&state=_default&response_type=code&code_challenge=4-QLwrs2LCzfJS6ezxw0pa2tykJFHb7x9_bbRm-jy2c&code_challenge_method=S256&access_type=online
Once we have the authentication code, insert it in the cell below.
# Add the authorization code that you got from Globus
auth_code = "CFnYvreOnCm0HXtBdat9RiiKdGO4kl"
# Exchange code for access tokens
response_token = native_auth_client.oauth2_exchange_code_for_tokens(auth_code)
# Split tokens based on their resource server
# This is the token that allows to create a flow client
# but is before the flow gets authorized, after which
# you get another (more powerful) access token code
tokens = response_token.by_resource_server
# Create a variable for storing flow scope tokens. Each newly deployed flow scope needs to be authorized separately,
# and will have its own set of tokens. Save each of these tokens by scope.
# Whatever is in this dictionary has passed the deployment authorization,
# meaning you do not need to authorize over and over each time you want to run the flow.
saved_flow_scopes = {}
# Add a callback to the flows client for fetching scopes. It will draw scopes from `saved_flow_scopes`
def get_flow_authorizer(flow_url, flow_scope, client_id):
return globus_sdk.AccessTokenAuthorizer(access_token=saved_flow_scopes[flow_scope]['access_token'])
# Setup the Flow client, using Globus Auth tokens to access the Globus Flows service, and
# set the `get_flow_authorizer` callback for any new flows we authorize.
flows_authorizer = globus_sdk.AccessTokenAuthorizer(access_token=tokens['flows.globus.org']['access_token'])
flows_client = FlowsClient.new_client(CLIENT_ID, get_flow_authorizer, flows_authorizer)
Configure the Globus Compute Client and Register our Function
Now that we have a function to run our analysis, we need to register it!
print("Instantiating a Globus Compute client ...")
gcc = Client()
# Register the function within the Globus ecosystem
print("Registering the Globus Compute function ...")
compute_function_id = gcc.register_function(run_plot_enso)
print(f"Compute function ID: {compute_function_id}")
Instantiating a Globus Compute client ...
Registering the Globus Compute function ...
Compute function ID: 72310e16-4dfb-43e5-884a-2c9d507ee711
Define our Flow
We need to define our flow - setting the expected parameters, and transferring the output html file at the end of the analysis. Notice we pass in the function ID we setup in the cell above.
flow_definition = {
"Comment": "Compute ENSO Index of a Given CMIP6 Model",
"StartAt": "RunPlotENSO",
"States": {
"RunPlotENSO": {
"Comment": "ESGF Search and Plot",
"Type": "Action",
"ActionUrl": "https://compute.actions.globus.org/",
"Parameters": {
"endpoint.$": "$.input.compute.id",
"function": compute_function_id,
"kwargs": {"source_id.$":"$.input.compute_input_data.source_id",
"return_path": True
}
},
"ResultPath": "$.ESGF_output",
"WaitTime": 600,
"Next": "TransferResult"
},
"TransferResult": {
"Comment": "Transfer files",
"Type": "Action",
"ActionUrl": "https://actions.automate.globus.org/transfer/transfer",
"Parameters": {
"source_endpoint_id.$": "$.input.destination.id",
"destination_endpoint_id.$": "$.input.destination.id",
"transfer_items": [
{
"source_path.$": "$.ESGF_output.details.result[0]",
"destination_path.$": "$.input.destination.path",
"recursive": False
}
]
},
"ResultPath": "$.TransferFiles",
"WaitTime": 300,
"End": True
}
}
}
Configure the Schema
We also need to define the schema, or what is expected, for our flow.
input_schema = {
"required": [
"input"
],
"properties": {
"input": {
"type": "object",
"required": [
"compute",
"destination",
"compute_input_data"
],
"properties": {
"compute": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Select source collection and path",
"description": "The source collection and path (path MUST end with a slash)",
"required": [
"id",
],
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "string",
"format": "uuid",
"default": endpoint_id
},
},
"additionalProperties": False
},
"destination": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Select destination collection and path",
"description": "The destination collection and path (path MUST end with a slash); default collection is 'Globus Tutorials on ALCF Eagle'",
"required": [
"id",
"path"
],
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "string",
"format": "uuid",
"default": personal_endpoint_id
},
"path": {
"type": "string",
"default": f"/plot.html"
}
},
"additionalProperties": False
},
# Compute function input data
"compute_input_data": {
"type": "object",
"title": "Input data required by compute function.",
"description": "Compute function input data.",
"required": [
"source_id",
],
"properties": {
"source_id": {
"type": "string",
"description": "Source Identifier for the model of interest",
"default": "CESM2"
},
},
"additionalProperties": False
}
}
}
}
}
Deploy the flow
We can deploy the flow as a test, passing in the default settings and schema.
# Deploy the flow
flow = flows_client.deploy_flow(
flow_definition,
title = "ESGF ENSO Test",
input_schema=input_schema,
)
We need a few parameters to actually run the deployed flow.
# Store flow information
flow_id = flow['id']
flow_scope = flow['globus_auth_scope']
flow_name = flow['title']
# Once deployed, the flow needs to be authorized
# If the flow scope is already saved, we don't need a new one.
if flow_scope not in saved_flow_scopes:
#if True:
# Do a native app authentication flow and get tokens that include the newly deployed flow scope
native_auth_client = globus_sdk.NativeAppAuthClient(CLIENT_ID)
native_auth_client.oauth2_start_flow(requested_scopes=flow_scope)
print(f"Login Here:\n\n{native_auth_client.oauth2_get_authorize_url()}")
# Authenticate and come back with your authorization code; paste it into the prompt below.
auth_code = input('Authorization Code: ')
token_response = native_auth_client.oauth2_exchange_code_for_tokens(auth_code)
# Save the new token in a place where the flows client can retrieve it.
saved_flow_scopes[flow_scope] = token_response.by_scopes[flow_scope]
# These are the saved scopes for the flow
print(json.dumps(saved_flow_scopes, indent=2))
Login Here:
https://auth.globus.org/v2/oauth2/authorize?client_id=16659080-53cd-45c7-8737-833d3e719f32&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fauth.globus.org%2Fv2%2Fweb%2Fauth-code&scope=https%3A%2F%2Fauth.globus.org%2Fscopes%2Fc65bffa0-bbea-4295-ab38-645eca9cdd54%2Fflow_c65bffa0_bbea_4295_ab38_645eca9cdd54_user&state=_default&response_type=code&code_challenge=ZqlFzOoWi3n_p3KFNF4T-HMsAAiR8rIawhUk6dRWsRM&code_challenge_method=S256&access_type=online
{
"https://auth.globus.org/scopes/632e1f8b-7e3e-4ffb-a055-cd388659d87c/flow_632e1f8b_7e3e_4ffb_a055_cd388659d87c_user": {
"scope": "https://auth.globus.org/scopes/632e1f8b-7e3e-4ffb-a055-cd388659d87c/flow_632e1f8b_7e3e_4ffb_a055_cd388659d87c_user",
"access_token": "AgM8lx1V0P02x8dJj6dG2Qx6a8K5gWWvlky6vkP4Dq0okEWMxVtOC2qeJPzjxoMpaK4qeOE88DOqlKCa671p6HPJ2Wz",
"refresh_token": null,
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_at_seconds": 1713467553,
"resource_server": "632e1f8b-7e3e-4ffb-a055-cd388659d87c"
},
"https://auth.globus.org/scopes/c65bffa0-bbea-4295-ab38-645eca9cdd54/flow_c65bffa0_bbea_4295_ab38_645eca9cdd54_user": {
"scope": "https://auth.globus.org/scopes/c65bffa0-bbea-4295-ab38-645eca9cdd54/flow_c65bffa0_bbea_4295_ab38_645eca9cdd54_user",
"access_token": "AgwwJ8rKnOVDdbYrD3Y99VWpY6gKq7jkyOrBy8qvEaopOMQJoHlCvlNQBMa95jdlyKG1E2rl0rWYGs8vqb0NSNbm7b",
"refresh_token": null,
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_at_seconds": 1713468049,
"resource_server": "c65bffa0-bbea-4295-ab38-645eca9cdd54"
}
}
Run the Deployed Flow
Once we setup the authentication, we can pass in our parameters and run the flow!
flow_input = {
"input": {
"compute": {
"id": endpoint_id
},
"destination": {
"id": personal_endpoint_id,
"path": f"/{os.getcwd()}/esgf_plot.html"
},
"compute_input_data":{
"source_id": "CESM2"
}
}
}
flow_action = flows_client.run_flow(
flow_id = flow_id,
flow_scope = flow_scope,
flow_input = flow_input,
label="Test local to local",
)
# Get flow execution parameters
flow_action_id = flow_action['action_id']
flow_status = flow_action['status']
print(f"Flow can be monitored in the webapp below: \nhttps://app.globus.org/runs/{flow_action_id}")
print(f"Flow action started with ID: {flow_action_id} - Status: {flow_status}")
Flow can be monitored in the webapp below:
https://app.globus.org/runs/dc2b4f0c-1ec6-4f70-ae15-0c33bbbfcffb
Flow action started with ID: dc2b4f0c-1ec6-4f70-ae15-0c33bbbfcffb - Status: ACTIVE
Here, we setup a check to ensure the flow is still running, and visualize the response when it finishes!
# Poll the Flow service to check on the status of the flow
while flow_status == 'ACTIVE':
time.sleep(5)
flow_action = flows_client.flow_action_status(flow_id, flow_scope, flow_action_id)
flow_status = flow_action['status']
print(f'Flow status: {flow_status}')
# Flow completed (hopefully successfully!)
print(json.dumps(flow_action.data, indent=2))
Flow status: ACTIVE
Flow status: ACTIVE
Flow status: ACTIVE
Flow status: ACTIVE
Flow status: ACTIVE
Flow status: ACTIVE
Flow status: ACTIVE
Flow status: ACTIVE
Flow status: SUCCEEDED
{
"run_id": "dc2b4f0c-1ec6-4f70-ae15-0c33bbbfcffb",
"flow_id": "c65bffa0-bbea-4295-ab38-645eca9cdd54",
"flow_title": "ESGF ENSO Test",
"flow_last_updated": "2024-04-16T19:20:37.184469+00:00",
"start_time": "2024-04-16T19:20:55.580835+00:00",
"completion_time": "2024-04-16T19:21:48.188000+00:00",
"status": "SUCCEEDED",
"display_status": "SUCCEEDED",
"details": {
"code": "FlowSucceeded",
"output": {
"input": {
"compute": {
"id": "6836803d-9831-4dc5-b159-eb658250e4bc"
},
"destination": {
"id": "92bb829c-9d88-11ed-b579-33287ee02ec7",
"path": "//Users/mgrover/git_repos/esgf-cookbook/notebooks/esgf_plot.html"
},
"compute_input_data": {
"source_id": "CESM2"
}
},
"ESGF_output": {
"label": null,
"status": "SUCCEEDED",
"details": {
"result": [
"/Users/mgrover/plot.html"
],
"results": [
{
"output": "/Users/mgrover/plot.html",
"task_id": "e7d42503-81c4-488b-a760-9846be264d6e"
}
]
},
"action_id": "tg_e81f1357-c21e-4a34-af82-6a2aa910bf0e",
"manage_by": [
"urn:globus:auth:identity:97c1da09-1d6d-4189-a5be-6ae3f85ae21f"
],
"creator_id": "urn:globus:auth:identity:97c1da09-1d6d-4189-a5be-6ae3f85ae21f",
"monitor_by": [
"urn:globus:auth:identity:97c1da09-1d6d-4189-a5be-6ae3f85ae21f"
],
"start_time": "2024-04-16T19:21:00.341325+00:00",
"state_name": "RunPlotENSO",
"release_after": null,
"display_status": "All tasks completed",
"completion_time": "2024-04-16T19:21:21.806350+00:00"
},
"TransferFiles": {
"label": null,
"status": "SUCCEEDED",
"details": {
"type": "TRANSFER",
"files": 1,
"is_ok": null,
"label": "For Action id IwD1kgdTb0Dn",
"faults": 0,
"status": "SUCCEEDED",
"command": "API 0.10",
"task_id": "833f2aaa-fc26-11ee-b703-473d136f742f",
"deadline": "2024-04-17T19:21:24+00:00",
"owner_id": "97c1da09-1d6d-4189-a5be-6ae3f85ae21f",
"symlinks": 0,
"username": "u_s7a5uci5nvaytjn6nlr7qwxcd4",
"DATA_TYPE": "task",
"is_paused": false,
"event_list": [
{
"code": "SUCCEEDED",
"time": "2024-04-16T19:21:31+00:00",
"details": {
"files_succeeded": 1
},
"is_error": false,
"DATA_TYPE": "event",
"description": "succeeded"
},
{
"code": "PROGRESS",
"time": "2024-04-16T19:21:31+00:00",
"details": {
"mbps": 0.46,
"duration": 4.08,
"bytes_transferred": 235449
},
"is_error": false,
"DATA_TYPE": "event",
"description": "progress"
},
{
"code": "STARTED",
"time": "2024-04-16T19:21:27+00:00",
"details": {
"type": "GridFTP Transfer",
"protocol": "UDT",
"pipelining": 20,
"concurrency": 2,
"parallelism": 2
},
"is_error": false,
"DATA_TYPE": "event",
"description": "started"
}
],
"sync_level": null,
"directories": 0,
"fatal_error": null,
"nice_status": null,
"encrypt_data": false,
"filter_rules": null,
"request_time": "2024-04-16T19:21:24+00:00",
"files_skipped": 0,
"subtasks_total": 2,
"completion_time": "2024-04-16T19:21:31+00:00",
"history_deleted": false,
"source_endpoint": "u_s7a5uci5nvaytjn6nlr7qwxcd4#92bb829c-9d88-11ed-b579-33287ee02ec7",
"subtasks_failed": 0,
"verify_checksum": false,
"source_base_path": null,
"subtasks_expired": 0,
"subtasks_pending": 0,
"bytes_checksummed": 0,
"bytes_transferred": 235449,
"canceled_by_admin": null,
"files_transferred": 1,
"source_local_user": null,
"subtasks_canceled": 0,
"subtasks_retrying": 0,
"preserve_timestamp": false,
"recursive_symlinks": "ignore",
"skip_source_errors": false,
"source_endpoint_id": "92bb829c-9d88-11ed-b579-33287ee02ec7",
"subtasks_succeeded": 2,
"nice_status_details": null,
"destination_endpoint": "u_s7a5uci5nvaytjn6nlr7qwxcd4#92bb829c-9d88-11ed-b579-33287ee02ec7",
"fail_on_quota_errors": false,
"destination_base_path": null,
"destination_local_user": null,
"nice_status_expires_in": null,
"destination_endpoint_id": "92bb829c-9d88-11ed-b579-33287ee02ec7",
"subtasks_skipped_errors": 0,
"delete_destination_extra": false,
"source_local_user_status": null,
"canceled_by_admin_message": null,
"effective_bytes_per_second": 30545,
"source_endpoint_display_name": "Work Laptop",
"destination_local_user_status": null,
"nice_status_short_description": null,
"destination_endpoint_display_name": "Work Laptop"
},
"action_id": "IwD1kgdTb0Dn",
"manage_by": [],
"creator_id": "urn:globus:auth:identity:97c1da09-1d6d-4189-a5be-6ae3f85ae21f",
"monitor_by": [],
"start_time": "2024-04-16T19:21:23.005698+00:00",
"state_name": "TransferResult",
"release_after": "P30D",
"display_status": "SUCCEEDED",
"completion_time": "2024-04-16T19:21:23.005728+00:00"
}
},
"description": "The Flow run reached a successful completion state"
},
"run_owner": "urn:globus:auth:identity:97c1da09-1d6d-4189-a5be-6ae3f85ae21f",
"run_managers": [],
"run_monitors": [],
"user_role": "run_owner",
"label": "Test local to local",
"tags": [],
"action_id": "dc2b4f0c-1ec6-4f70-ae15-0c33bbbfcffb",
"manage_by": [],
"monitor_by": [],
"created_by": "urn:globus:auth:identity:97c1da09-1d6d-4189-a5be-6ae3f85ae21f"
}
Summary
In this notebook, we applied the ENSO 3.4 index calculations to CMIP6 datasets remotely using Globus Compute and created interactive plots comparing where we see El Niño and La Niña.

